Safety Assurance And Failure Scope
by Nataliia Vasylyna | December 12, 2011 10:00 am
Note: the article was updated in September 2018.
Safety-critical systems are those, that can cause injury or even loss of user’s life in case of failure. Such systems can damage an equipment or environment as well. Previously, safety-critical systems were mostly related to engineering. But today, as far as engineering became computer-based, safety-critical systems has penetrated the IT industry.
In modern life, we deal with safety-critical systems all the time. They are used in medical care, nuclear power, aviation, automotive, weapons, space flights, and many other fields.

A good example of such a system would be a microprocessor that controls an insulin pump. Also, computers are used a lot in surgery procedures, e.g., spinal and ophthalmic surgery. Software control devices replace traditional surgery tools and provide a lot of benefits for patients.
Testing of Safety-Critical Systems
Because the failure of safety-critical systems can cost a lot and be very dangerous, they are created as accurate as possible. Coding, documenting, testing and analyzing must all be done very carefully and scrupulously.
As far as the quality of safety-critical systems should be very high, special attention is paid to the testing process. All the errors and issues should be eliminated from the system before its release to the market. If testing is not done properly, customers may face really awful consequences. The company, in this case, will pay criminal penalties or can be even sued.
There are special recommendations to adhere to while testing safety-critical systems:
- Testing should be conducted strictly according to the specification[1]
- All the issues and hazards should be identified in the early stages of the development cycle
- Independent verification is required
- All the threads should be reduced to an acceptable level
Among the techniques used for safety-critical systems are:
- White-box Testing
- Black-box Testing[2]
- Dynamic and Static Analysis
- Reviews
Also, aside from ordinary software testing techniques[3], several specific procedures are applied as well.
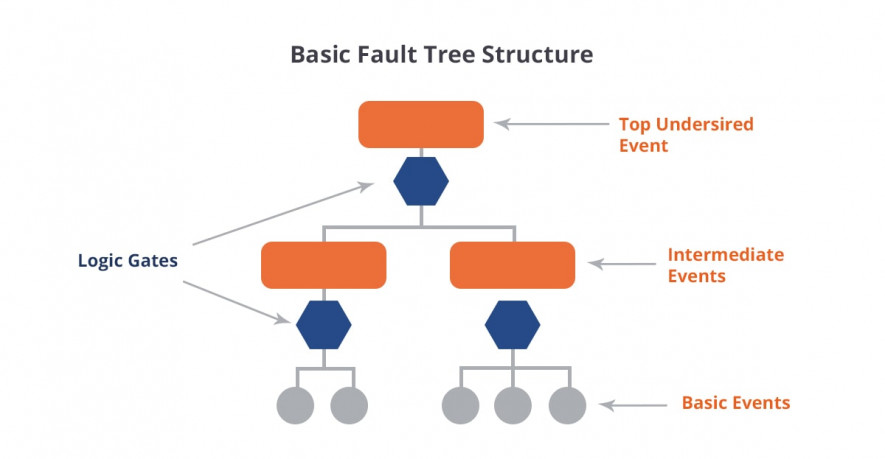
Fault Tree Analysis is one of the techniques of failure analysis. It is a graphical technique, which describes all possible combinations of occurrences in the system that can result in failure. The undesired effect is placed in the root of the tree, and its probability can be determined using mathematical techniques. Contributory failure events lead to the top level one.
Also, there are activities based on analysis of hazards or logical pre-conditions for accidents:
- Damage control through escape routes, safe abandonment of products and materials, and devices for limiting physical damages to equipment
- Hazard removal through replacement, simplification, decoupling, removal of particular people’ mistakes and a decrease of hazardous materials or conditions
- Hazard diminution through design for controlling, use of locking devices and defect[4] minimization using safety margins and superfluity
- Hazard control through lessening exposure, isolation and containment, protection systems, and fail-safe design
Both hazard control and damage control are post-failure activities that attempt to include the defects so that they will not lead to accidents or the accident damage can be controlled or minimized.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- specification: https://qatestlab.com/resources/knowledge-center/sample-deliverables/
- Black-box Testing: https://qatestlab.com/resources/knowledge-center/black-box-testing/
- software testing techniques: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/03/01/software-testing-techniques/
- defect: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/10/11/main-types-of-defects-in-software-testing/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/12/12/safety-assurance-and-failure-scope/

