Difference Between White Box, Black Box, and Gray Box Testing
by Nataliia Vasylyna | March 1, 2011 4:00 pm
Note: the article was updated in September 2018.
In this article, we are going to talk about three common approaches to software testing: white-box, black-box, and grey-box testing. We will find out the benefits of each of these approaches and their main specific features.
Black-box testing
Black-box method[1] is a testing approach when QA specialists have no access to the source code or the internal structure of software. The main goal of this testing type is to check whether everything works well from the point of view of an ordinary user.
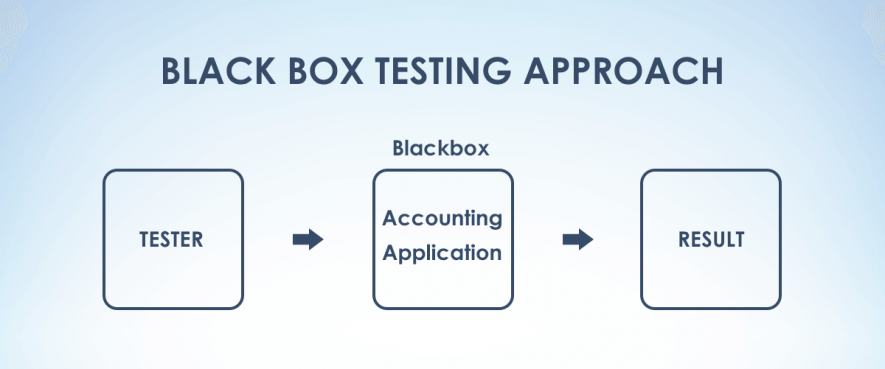
Main features:
- it doesn’t require the understanding of the software internal structure
- test design is elaborated according to the software specification
Focuses on:
- incorrect or missing functions
- GUI errors
- data structures errors
- inadequate software performance
- control flow errors
Test design techniques based on black-box testing:
- equivalents classes
- boundary values analysis
- decision tables[2]
- state changing diagrams
Advantages of black-box testing:
- no need for a tester to know the programming language of the application
- tests preparation time is short
- testers start designing test cases just after the specification is ready
- testers can notice some specification contradictions
Disadvantages of black-box testing:
- only some random paths are covered
- it is impossible to anticipate what part of the code can cause a problem in future
- it is hard to design test cases without a specification
- lack of information for detailed testing
White-box testing
White-box testing is a testing approach when QA specialists have an access to the source code and internal structure of the software. This testing type implies that a tester knows which code line is called for each functionality. It gives an opportunity not only to better choose an entry data set but also to check errors and exceptions handling.
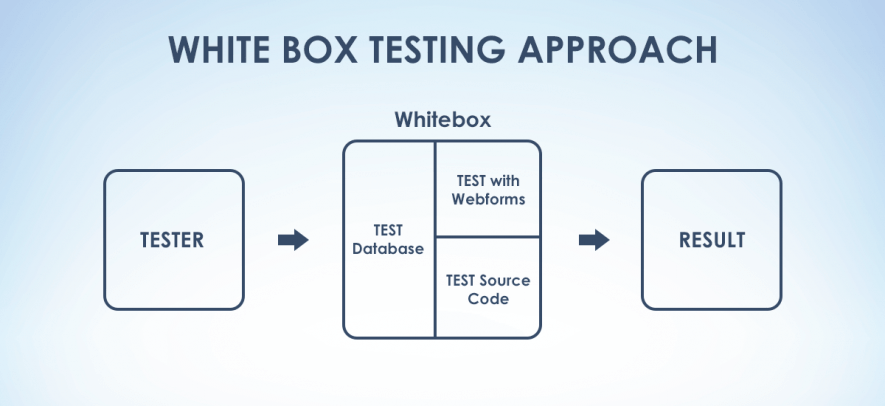
The main features of white-box testing are:
- test cases are based on the system internal structure analysis
- proper for unit tests, integration tests, and system tests
- the expected result is clear
Focuses on:
- bad code writing practices
- security holes[3]
- the functionality of conditional loops
- working flow of the code
- memory leaks
Test design techniques based on white-box testing:
- statement coverage
- branch coverage
- path coverage
- function coverage
Advantages of white-box testing:
- testing can be conducted in the early stages of the software lifecycle
- no need to wait for the GUI implementation
- it is possible to conduct more detailed testing with more cases covered
- it is possible to anticipate the potential problems
Disadvantages of black-box testing:
- a tester must know the programming language of the software
- takes much more time than other approaches
- can be complex and expensive
Grey-box testing
Grey-box testing is a testing approach when the testers have only a partial access to the internal structure. Often it includes databases and the information about algorithms used, though it depends on the case. Still, testing is done from the point of view of an ordinary user like in the case of black-box testing.
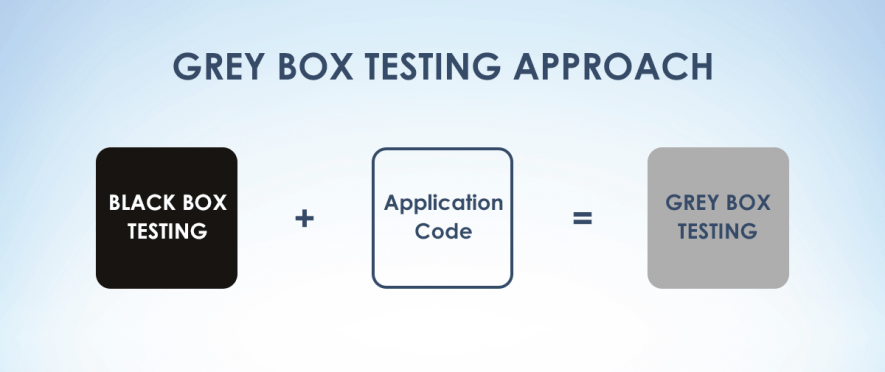
Main features:
- test design is based on the data structures and algorithms knowledge
- actual tests are conducted using the exposed interfaces
- a tester can have an access to the source code for test cases design
Test design techniques based on grey box testing:
- matrix testing
- regression testing
- orthogonal array testing
- pattern testing
The grey box testing incorporates advantages and disadvantages of white-box and black-box techniques and can be a good compromise in the question which of the techniques to choose.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- Black-box method: https://qatestlab.com/resources/knowledge-center/black-box-testing/
- decision tables: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2016/02/23/decision-table-testing/
- security holes: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2018/04/05/data-breaches-statistics/
- What Is The Difference Between White Box, Black Box And Gray Box Testing?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/11/21/what-is-the-difference-between-white-box-black-box-and-gray-box-testing/
- Black Box Test Techniques. Random Testing: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/09/19/black-box-test-techniques-random-testing/
- Software Testing Techniques: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/03/01/software-testing-techniques/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/03/01/difference-between-white-box-black-box-and-gray-box-testing/

