6 Basic Criteria For Testing Requirements
by Tetyana Lykhitska | May 7, 2011 10:00 am
Note: the article was updated in September 2025
When testing requirements is overlooked, QA teams lose alignment between product functionality and business objectives. This results in inconsistent test coverage, undetected defects, delayed feedback loops, and unstable release cycles. For the business, this means missed deadlines, higher costs, and a damaged product reputation.
That’s why our software testing services begin with requirement definition, ensuring they are complete, consistent, and testable. This approach allows us to create accurate and complete QA documentation. Moreover, it gives clients a clear view of progress, a controlled testing process, and confidence in product readiness.
Read this article to get clear criteria for validating software requirements and find out why these principles are critical for building reliable quality assurance processes and delivering successful products.
Why is Requirements Testing Important?
Requirements-based testing means that test cases, test plans, and checklists are built directly from documented and agreed-upon specifications. This approach helps streamline team workflows and minimize potential misunderstandings. Verifying requirements at the early stages of development contributes to the overall quality of the software solution. As a result, the client receives a reliable and competitive product built in full compliance with the defined expectations.
What Happens if Testing Requirements are Avoided?
Inaccurate quality assessment – If there’s no agreed reference for expected behavior, it’s impossible to objectively assess product quality, making test results unreliable.
Wasted time and resources – Unstructured testing efforts often cover irrelevant areas or skip essential ones, resulting in wasted team effort and reduced efficiency.
Failure to detect critical defects – Without a clear understanding of business priorities, testers may miss key risk areas, allowing serious bugs to go unnoticed.
Lack of shared understanding – Misaligned expectations cause teams to interpret the same requirement differently, leading to functionality gaps, costly rework, and prolonged testing cycles.
Low confidence in product readiness – When there is no baseline for validation, testing doesn’t provide confidence that the product solves real user needs, putting credibility and market perception at risk.

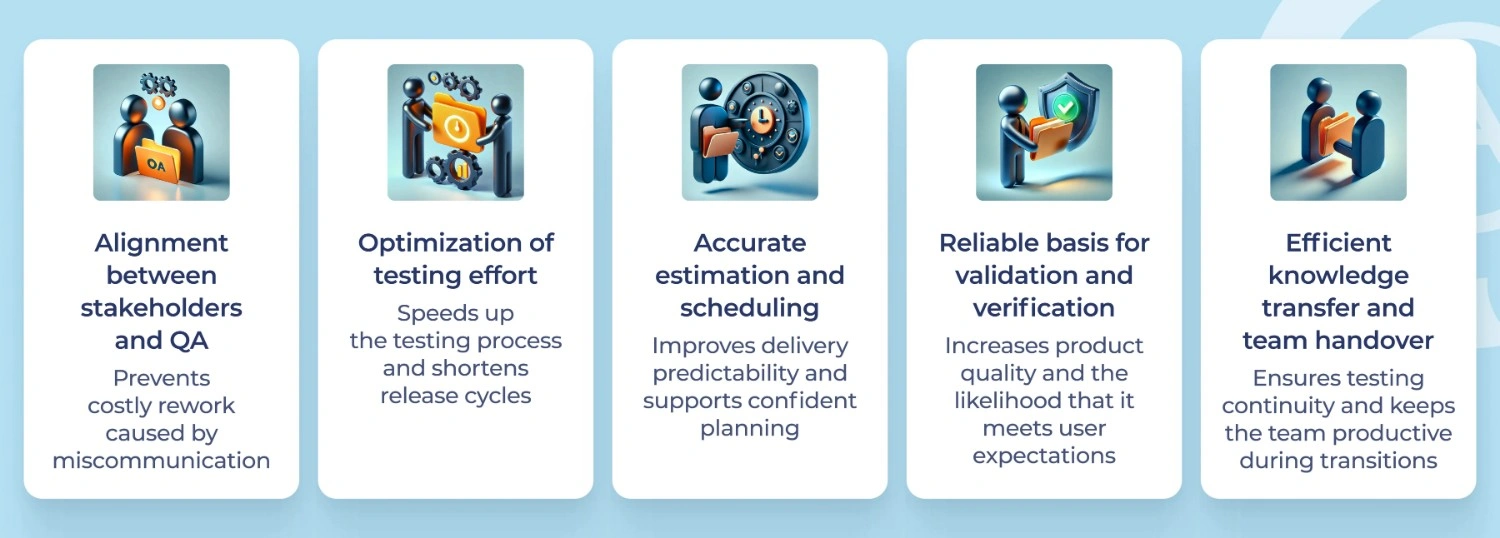
Advantages of Requirements-Based Testing
Let’s look at the key benefits of starting the QA process with clearly defined requirements:
- Establish a clear, shared understanding across teams, allowing QA to work with well-defined expectations.
- Reduce the number of unnecessary or irrelevant tests, minimizing overall testing effort.
- Enable accurate estimation of testing scope and realistic scheduling.
- Provide a solid basis for verifying whether the implementation meets the specified requirements.
- Simplify task handover and support consistent documentation when team members change or the project scales.
As you can see, when QA teams are able to plan and test effectively, it also has a positive impact on the overall success of the product. Early defect detection, reduced rework, and faster cycles lead directly to improved delivery timelines, lower costs, and higher user satisfaction — all of which are critical business goals.
The List of Basic Testing Requirements
Static testing of specification requirements relies on six key criteria that confirm completeness, clarity, consistency, traceability, feasibility, and testability. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
Completeness
All requirement components must be present and clearly described to be considered complete. When testing the specification set for completeness, testers should pay particular attention to the following:
- Requirements should not contain vague expressions such as “and so on,” “others,” or “the like.”
- They must not refer to non-existent sources, such as a missing specification[1].
- Specifications should not rely on functionality that is undefined.
Unambiguity
Each requirement must be legible, stated clearly and precisely to allow only one possible interpretation. If a specification is particularly complex, supporting materials such as diagrams or tables may be used to aid understanding. Avoid vague expressions like “it’s obvious” or “self-evident,” as they can conceal ambiguity and hinder shared knowledge.
Consistency
Specifications should be consistent with one another and comply with current standards. If any conflicts arise, priorities must be defined to resolve them. Identifying the impact of any violated requirements demands a solid understanding of the specification document and familiarity with relevant standards or external references.
Traceability
Each requirement must have a unique identifier to ensure traceability throughout the development lifecycle. In later-stage work products, such as the test plan[2], every reference to a requirement should be clearly traceable back to its original definition and specification.
Feasibility
Each requirement should define the system tasks necessary to support both development and ongoing maintenance. Unrealistic demands regarding timelines, budgets, or functionality, particularly those that may result in unreliable or unsafe features, must be treated as risks and addressed early. Ultimately, the system should be economically feasible, reliable, user-friendly, and easy to maintain.
Testability
It should be possible to develop cost-effective and practical tests for each requirement to demonstrate that the software possesses the required functionality, performance, and compliance with applicable standards. Each specification must be measurable, and testing should be conducted under acceptable conditions.
Once requirements are validated, the next step is turning them into test cases. If you also need useful advice on creating this type of documentation, visit our blog to read the article What are the Main Attributes of a Test Case?[3]
Conclusion on Testing Requirements
A core goal of software testing is to prevent bugs and defects from reaching production. Testing requirements for future software[4] is a reliable solution to avoid mistakes during the development stage. It is when the continuous testing starts, to guarantee the required quality of the developed software and eliminate possible business risks.
We hope that the above testing procedure template will assist you while preparing the requirements, and that advice from QATestLab testers will be useful for your project.
Also, if you want testing that truly reflects your requirements and contributes to your product’s success, contact us[5]. We’ll make sure your QA process supports your goals, helps you stay on schedule, and delivers confidence at every stage. We’re always happy to assist you in releasing with clarity and control.
 [6]
[6]Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- specification: https://go.qatestlab.com/sample-deliverables
- test plan: https://go.qatestlab.com/test-plan
- What are the Main Attributes of a Test Case?: https://go.qatestlab.com/main-attributes-of-a-test-case
- Testing requirements for future software: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2015/01/09/why-is-it-wise-to-test-software-requirements-before-writing-the-code/
- contact us: https://go.qatestlab.com/requirements-testing
- [Image]: https://go.qatestlab.com/requirements-testing
- What to Do if Requirements Are Changing Constantly?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/08/15/what-should-you-do-if-requirements-are-changing-constantly/
- How to Test without Specification: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2017/10/19/test-without-specification/
- Does Your Project Need a Test Plan?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2017/04/17/test-plan-importance/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/05/07/6-basic-criteria-for-testing-requirements/

