Beyond the Reality: Challenges of VR Apps Testing
by Asha Jane Brown | April 2, 2019 9:56 am
The future is already here. Artificial intelligence has turned now into reality and became a part of our life. Modern software not only respond to our voice and recognize our faces but poses new challenges to QA and testing[1]. Today we are going to reveal the potential of Virtual Reality software. We will also share own experience on the difficulties that may occur while testing them.
Not Games Only: Industries that make use of VR
According to Statista, by 2020 the Worldwide Virtual Reality Market will reach 14.5 billion dollars.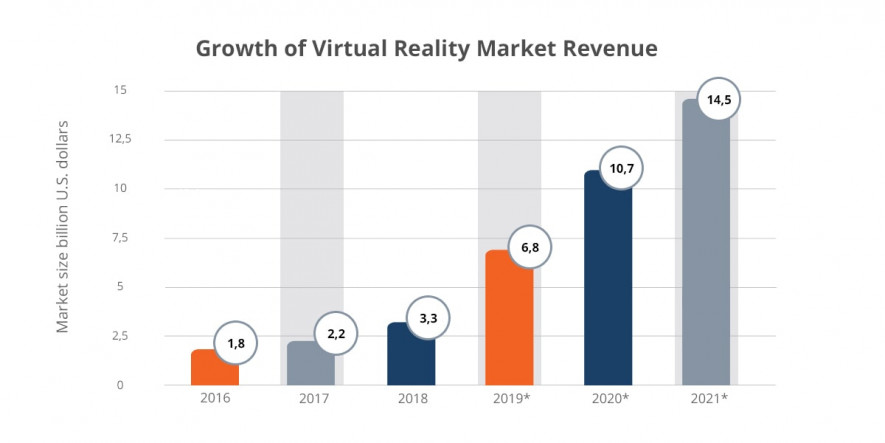
This technology is widely recognized in the game industry[2], but its sphere of implementation goes far beyond games. VR can simulate almost any type of real space. It can be used in Education, Engineering, Video, Real Estate, Retail, and Military.
Another promising sphere for VR application is Healthcare. This software is used in surgery to create 3D models and plan operations. In psychotherapy, it helps to treat mental diseases, phobias, and anxiety disorders.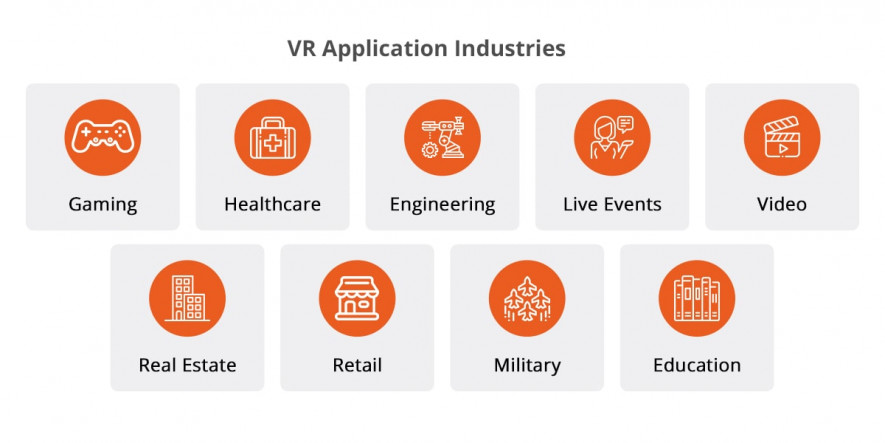
Despite the popularity of VR applications, this technology is still at the stage of its development. It has specific bottlenecks that may cause a lot of damage if not properly tested. What are these bottlenecks and how to avoid them?
Risks and Challenges of VR Applications
Probably, VR issues are not so crucial in case of games. But what if during surgery it turns out that the 3D model is defective? Who will take responsibility for the consequences? This makes VR software manufacturers pay special attention to the quality of their products and require their professional testing.
According to QATestLab experience, the most widespread VR bugs include functional problems, motion issues and collisions of objects. All these challenges can be grouped as connected with:
- health impact
- non-standard interfaces
- compatibility issues
- motion testing
- extra space
- test automation
Health impact of VR apps
Physical nature of VR wearables can have a negative impact on a user[3]. Headaches, sickness, eye strain, seizures, visual difficulties are common effects of VR technology.
“Eyes start to hurt after a day of VR testing, especially if the pictures in the game are of low quality. I would recommend to blink more often while wearing a helmet to moisturize your eyes and avoid unpleasant feelings,” – shares Alexey, QATestLab VR test engineer.
“Also, when you wear the helmet for a long time, there is a strange feeling that you lose touch with reality. Sometimes, you can feel motion sickness. It occurs when the movement is based on the use of Locomotion technology, or if the player’s vestibular apparatus is not trained,” – adds our specialist.
Possible ways out. A good practice is to have breaks every 30 minutes of testing so that the body could rest.
Alexey also explains: “Breaks must be done frequently otherwise you can get tired or feel sick very quickly. During breaks, we usually report bugs, write down necessary checks and issues to pay more attention to”.
It is a good practice to have another tester to supervise the whole process and prevent injuries of the first one. At this point, accessibility testing can help to determine the level of application immersion when the user’s discomfort is minimal.
Non-standard interfaces
Another challenge is conducting GUI and usability testing. Usually, GUI testing covers such common elements as windows, menu, and icons. But VR apps[4] go beyond standard interfaces and allow users to interact with the application in 3D space. Instead of buttons and touchscreen, you use your body positions and controllers. Testing team should be prepared to face such challenges and take special training before working with VR.
Compatibility issues
Some platforms and devices can greatly slow down the performance of the VR application. Moreover, devices can undergo such problem as overheating. These aspects should be properly checked and controlled.
Motion Testing
Motion Testing ensures that all the digital data generated by user motions are accurately processed and imposed on the VR image. Motion problems can be caused by both, hardware and software issues. As a result of such problems, you can see objects floating from their intended positions.
“Passing through the walls is one of the most common problems in VR testing. Using a controller, a user comes close to the wall and can move through it. Another possible issue is to fall down through the floor. The problems are usually caused by poor synchronizing of movements,” – explains our test engineer.
During motion testing, we recommend to do as much unexpected and unpredicted movements as possible. This helps to ensure that the app deals with different situations in a proper way.
Extra space for testing
Testing VR applications requires extra space around the tester. This helps to make the testing process[5] comfortable and accurate.
QATestLab specialist explains this request: “For VR testing, we use sensors, that fix the position of the helmet and controllers. Moreover, testers need space for movements. The best decision is to equip a separate room for testing VR applications.”
Test automation
VR apps testing is all about human perception, so when it comes to test automation, it is pretty hard to implement it, at least for now. As a result, manual testing is performed during the whole testing process.
Last word on Testing VR Applications
Talking about the quality of a VR app, we talk about the safety and health of its users. That is why testing and QA activities[6] should be an integral part of VR app development process. To be sure in the quality of the software you produce, entrust your product to an experienced QA provider. This way you will get the necessary devices, and the team prepared to handle all the peculiarities of working in VR environment.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- QA and testing: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/04/07/what-is-the-difference-between-qa-and-testing/
- game industry: https://qatestlab.com/solutions/by-focus-area/games/
- impact on a user: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2018/12/26/online-casino-testing/
- VR apps: https://qatestlab.com/services/special-offer/virtual-reality-solutions/
- testing process: https://qatestlab.com/approach/technologies/
- QA activities: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2011/12/21/quality-assurance-activities-in-software-processes/
- Initiating Automation Testing in the Digital Era: Decoding Its Significance and the Wisdom of Vendor Collaboration: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2023/10/25/initiating-automation-testing-in-the-digital-era-decoding-its-significance-and-the-wisdom-of-vendor-collaboration/
- When Does Your Project Need Test Automation?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2023/04/12/when-automate-testing/
- How to Test Marketing Automation Software: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2021/07/14/how-to-test-marketing-automation-software/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2019/04/02/testing-vr-applications/

