Differences between Web App and Mobile App Testing
by Vadym Yudovych | June 18, 2019 6:54 am
Still doubt if your software needs a mobile version? Let’s think: 3.7 billion people have mobile phones, and 47.96% of them use mobile applications. Are you ready to lose approximately 2 billion of possible users?
Fortunately for users, the modern market offers advanced technologies so often that it became not a surprise, but a predictable trend.
We got used to being always online, and we do not want to log in and log out every time. It became easy to be online as long as we want due to mobile apps. Approximately half of the total software is released with bugs, it is both web and mobile applications. This is the reason why testing becomes an integral part of product development[1], but is there a difference between testing its web and mobile version? Let`s find this out.
What is Web App Testing?
Web testing aims to check and detect websites and web applications. It is full testing of web-based programs before bringing them to live for end users.
The main elements of Web testing are UI design and functionality testing accompanied by Compatibility, Performance, Security and Usability Testing. Their aim is to define the potential server load, type of performance, which is required for each load condition and testing tools. You should also know who is the end-user, what type of browser will be used, and what the connection speed will be. It is necessary to define apps usability and speed of program reaction.
What is Mobile App Testing?
This type of testing is focused on the proper performance of the app on the chosen mobile device. It is important to test each mobile product under different levels and quality of network connection. QATestLab specialists, for example, examine if the system can handle high loads[2] during stress, load, and performance testing.
Mobile testing has a wider scope of examination, as the objects of testing are mobile devices with various system requirements. The variety of mobile devices in QATestLab includes 250 gadgets with different parameters for testing purposes. Tests check both “native” mobile and web apps which are set up and redesigned for mobile use. Mobile testing includes verification of proper work of apps in different ways of user`s interactions, different capacity, condition, and abilities of mobile devices.
Mobile and Web Application Testing: Differences
It is clear that both testing activities have their common goal, which is to ensure the functionality in different circumstances. Now, let`s look directly on the differences between web and mobile app testing[3], depending on the permanently growing mobile technologies:
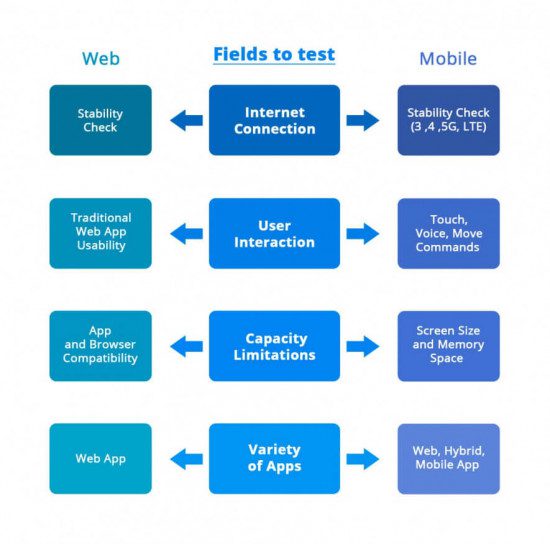
Internet Connection
In most case, web apps can be used only being connected to the Internet. Not many apps can bring a benefit in offline mode, only some default office programs, as an exception. Usually, desktops use the internet connection, which is stable and the thing that should be tested is the speed of connection and whether the certain program is completely functional with available speed.
In its turn, for mobile devices, it is not enough just to have a connection. It should be clarified if the work is proper with 3, 4, 5G or WI-FI, how the distance impacts the quality of connection, how the work of the app reacts on breaches of connection, restarts after breaches and low connection, what is the speed of LTE connection.
User Interaction
Desktop users got used to performing almost all operations through clicking, and browser-based applications are usually limited to keyboard and mouse. On the other hand, mobile apps widen the freedom of actions so much, that possible options are sometimes even hard to remember. The usual touch screen is now accompanied by voice assistants and move commanders. Such tool as Siri develops faster than some of the fields of science and proves that voice control becomes a part of everyday life.
Considering the variety of new options, testing should focus on the abilities of mobile devices to interact with user`s moves, eye moves, the direction of user`s attention, voice and even environment and check if the program recognizes all these factors as they really are. All the way of interaction must be tested to ensure their expected work.
Capacity Limitations
Web applications are more simple in use due to the functionality of the device, and usually, it is a desktop. This means that the user may not worry about limitations which are so annoying in smartphones. What drives you crazy the most? Right! The low battery. Testing should check the usability of the app in case of fully and low charged device. But that is not the only issue.
QA team[4] should also consider such parameters as RAM and SSD, which are absolutely different in web and mobile fields. The capacity of even the most advanced smartphones is out of comparison with abilities, which PC can offer. Here it is important to check how the app affects the memory. In case of mobile devices, it is especially relevant, because mobile apps are often subjected to numerous repeatable installations and updates, which requires enough free space. Also, it is necessary to test the behavior of a certain app after several installations and updates in different versions, as the compatibility is often limited to different versions of smartphones unlike in case of desktop operating.
Another issue is visual and multitasking capacity. Several web applications are possible to be reproduced on the PC at the same time. It is also possible on a smartphone, but the screen size does not allow to combine different activities as well as operate them simultaneously. That is why the functionality of the mobile app should be tested with its ability to be properly reproduced. Specific mobile screen dimensions should be examined to ensure that all the fields are visible and accessible. Nowadays, there are mobile devices which impress by its ability to transform and change the parameters of the screen resolution to combine a few different functions, but in this case, it is also necessary to examine the behavior of the app in comparison with others and in various screen settings.
Variety of Apps
In case of Web apps, it is easier to be confident in the right choice because the usability of web apps depends on browser type and software version if we talk about PC. The user is quite limited in his choice but has not to worry about compatibility issues. Despite stable relations of web apps and desktops, mobile apps impress by their variety, and there is much work to do for compatibility testing. Mobile apps include Native, Hybrid, and Web apps, which are set up for mobile purposes. All these types should be checked on their compatibility with a mobile device, and this task is difficult due to the fact that every brand of smartphones has many versions of a device with its specific settings.
To Make a Conclusion on Web and Mobile Testing
The main goals of testing are still the same despite the variety of objects for testing. However, the differences of web and mobile applications must be attentively considered because the numerous peculiarities of both fields show that the proper testing of web application does not mean the successful functioning of a mobile app in case of using the same testing approach towards different apps. As modern trends show, mobile apps should be examined more carefully because the setting and options which can be applied in mobile devices are much more various than the desktop environment. That is why quality assurance requires a qualified approach which can be provided with expert tips of QATestLab specialists. Be sure you will not get lost in differences with our assistance and more useful material available in our blog.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- integral part of product development: https://qatestlab.com/services/
- handle high loads: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2015/09/23/about-load-testing/
- app testing: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2018/12/20/mobile-streaming-applications/
- QA team: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2019/05/07/building-qa-team/
- Is Source Code Really Necessary for Successful Automation?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2023/08/31/source-code-for-automation/
- Digitocracy: the state in a smartphone on the example of Ukraine: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2023/02/22/the-state-in-a-smartphone/
- Methods of Web Applications Testing: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2015/08/10/methods-web-applications/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2019/06/18/web-mobile-application-testing/

