Agile Testing Top 10 Practices: How to Improve Release Management?
by Kate Libbie | June 4, 2020 1:34 pm
For software testing, the central idea behind agile practices is simple: to ensure flexible, and bug-free code, high test coverage, and greater productivity of the tests. But if to look more closely, the task of conducting these practices is not as easy as it may seem. Knowing all the rules and nuances of these practices is mandatory both for QA testing engineers and product owners as well. Let’s summarize all these practices and learn how to conduct them.
Agile testing method: bits and pieces of the meaning
“The ability to create and respond to change to succeed in an uncertain and turbulent environment.” – Agile Alliance[1]
In current circumstances, when everything is changing rapidly, software development is instead a bespoke process and not a specialty occupation, turning an idea into ready-to life products is a big challenge. For this reason, Agile practices comes in handy during the Software development life cycle both for developers and QA engineers to succeed in the time of turbulence.
In its nutshell, Agile is a particular philosophy. It is not a secret technique that does wonders and turns bad products into good ones. It is just an approach to organize work, analyze all the tasks, estimate possible risks and set the correct system that will contribute to the team’s productivity. If you have a great idea and a powerful team, Agile practices will help to achieve goals faster through the discovery of what can put the entire peace process on hold, and what is, in turn, has a positive impact. At the same time, a struggling team might struggle even more with Agile.
Agile is the most popular technique – 89% of development models are powered by it, and this is for a good reason. If to compare Agile practices with traditional waterfall methodology, you can see significant leapfrog between these two systems. The traditional approach, which is also called Waterfall, has a variety of drawbacks in its algorithm. It is a linear sequence of events implying strict performance one step after another, where each stage generally finishes before the next one can begin. Here how it usually works: Requests > System Design > Implementation > QA & Testing > Deployment stage > Maintenance.
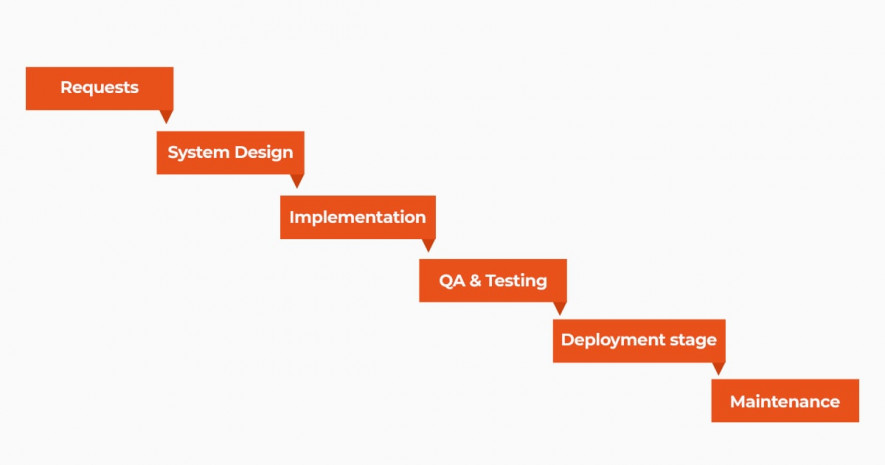
Such an approach can very quickly bring down the whole system if, for example, an error occurs in 1 step, and your team is already finishing 3 steps. Such cases are common in the current state of SDLC, where everything can change every minute. To resolve issues like this, a team using traditional methodology is usually forced to either going back or completing the redo entire scope of tasks again, which results in losing a huge amount of time and costs. If speaking about QA engineers routine, it is filled with so many cases when new bugs are arising again, and again. With a traditional approach, solving them is a total disaster.
Agile Testing: 10 practices to make testing more efficient
Learning how this methodology works for QA & testing is impossible without reading the legendary book Agile Testing: A Practical Guide for Testers and Agile Teams[2] crafted by L. Crispin and J. Gregory. The central attention in this book is paid on 10 practices that make a good ground for successful SDLC in Agile. To save your time, we tried to summarize these practices-rules and deliver the prime meaning for each of them. We hope it will help you grasp this material faster, and anytime you can go back and read more info from the book:
- The power of feedback. Agile QA engineers do not merely test but provide detailed feedback every time they found something (both for customers and developers). The art of explanation results that were obtained during testing plays a crucial role in the all subsequent fate of a product.
- Value for customers. The prime goal for any testing specialist working in Agile is not to find a great number of bugs, but to deliver value for customers. The quantity doesn’t equal quality. The end purpose of testing is not just testing, but contributing to product success, and finding all the possible pitfalls that prevent the application from this.
- Open communication. Communication can be especially hard when there is a need to talk with developers. The vast majority of testers strive to avoid such a dangerous confrontation, but not testing specialists in Agile, who understand all the importance and step into oped dialogue with developers.
- Be humble, embrace your courage. This one is born out of the previous rule. To set a successful confrontation with a developer, a tester should have great courage to prove any point he/she has, and be humble to do so.
- Simplicity is the key. Sometimes the most complex problems require simple solutions. Taking small steps in everyday routine, the testing specialists can focus solely on the necessary tests. After all, a big problem can be divided into small snippets, and so solved faster.
- Always ascending. If you don’t make progress, you start to go backward. QA engineers in Agile are keen learners, cause there is always new stuff to learn. The world of technology is continually growing, and QA needs to know all the nuances of the product he/she test.
- Be flexible. The ability to adapt to new products is precious in cycles of Agile. You should always keep up with the changes and don’t stick only at one thing.
- People first. No matter what problems you face, if you are working in Agile, first of all, you need to care about people. You can get much more valuable info from your colleague. That’s why QA specialists in Agile are collaborative, preferring human interaction over technology.
- Organize work better. Everyone can achieve better results after proper analysis of the good and bad sides of the performance. Organizing work is finding the right balance between what you can do and what you desire to do. Without the organization of tasks and time, very often an employee gets bogged down in duties and may stop growing.
- Do what you love. Agile testers who enjoy the work are able to deliver the greatest possible value to the customer.
On top of these, Agile practices also include Sprint planning, stand-ups meetings, and retrospectives, which is also similar to SCRUM[3]. These simple yet powerful Agile practices won’t make you wait long to see better results in your daily routine. By the way, these rules are also applicable not only for testing engineers but for all the other specialists as well.
 [4]
[4]
Agile Testing Quadrants: Easy way to predict your next step
Another critical aspect of Agile methodology for testing is Quadrants that help to understand what to do in short retrospective like what type of testing to conduct, what tests to run, etc. Here how it works:
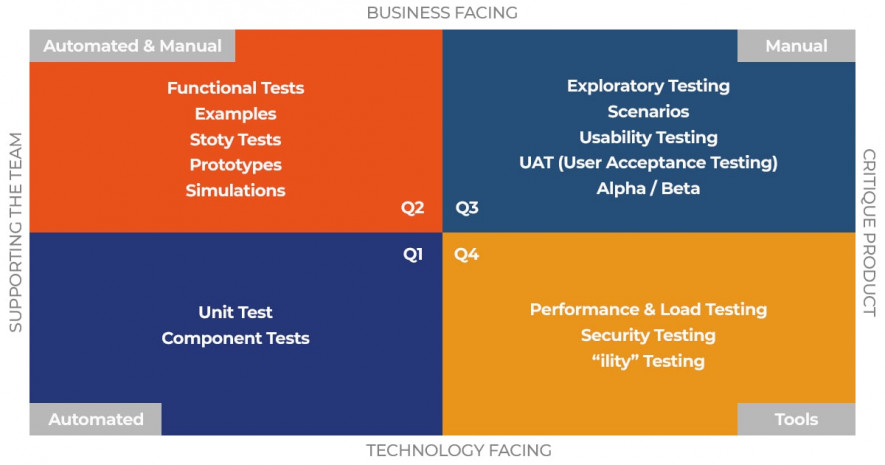
More precisely, each of the elements has the following meaning and purpose:
- Q1: Test Automation to improve the code.
- Q2: Test Automation + Manual to improve business outcomes.
- Q3: Manual tests to provide detailed feedback on product performance, functionality, and user experience. (often it is rechecking things done in Q1 and Q2)
- Q4: Tools to ensure security and compatibility.
Agile practices help to discover bugs faster and identify problems that can be solved by a programmer. All this contributes to a successful release.
Conclusion
To summarize: The Agile approach is centered around the idea of iterative development with open communication with colleagues and developers. Ultimately, Agile testing practices allow delivering more value to any product, and at the same time, empower the QA testing team, give motivation, and provide a favorable environment for growth. At the same time, project managers should take into account the following thing: without already high functioning and motivated team, Agile will be powerless.
……………………………
If your products are requiring testing, we are ready to hedge your team and ensure the high quality. We are participating in the life of the product, and do our work with a passion for your success. Let’s make great products together.
Visit our blog[5] to read more about QA & testing. Feel free to contact us[6] for collaboration.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- Agile Alliance: https://www.agilealliance.org/agile101/
- Agile Testing: A Practical Guide for Testers and Agile Teams: https://www.amazon.com/Agile-Testing-Practical-Guide-Testers/dp/0321534468
- SCRUM: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2020/05/26/scrum-testing/
- [Image]: https://qatestlab.com/services/?utm_source=Blog&utm_medium=Post&utm_campaign=services
- blog: https://blog.qatestlab.com/
- contact us: https://qatestlab.com/company/contacts/
- Assessing Success of Agile Project: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2016/08/17/agile-project-success/
- How to Reprogram a Mindset before Accepting Agile Principles?: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2016/06/07/accepting-agile-principles/
- Agile or Not: Tips to Determine a Team’s Approach to Product Development: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2016/04/20/alige-product-development/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2020/06/04/agile-testing-practices/

