Digitocracy: the state in a smartphone on the example of Ukraine
by Alyona Kolesnikova | February 22, 2023 8:50 am
Worldwide, more people have access to mobile phones than to proper sanitation. The International Telecommunication Union estimates that of the 7 billion people on earth, around 6.5 billion have access to a mobile phone. As of 2018, 100% of the population in low- and middle-income countries had access to mobile phones[1], whereas 55% of the people in low-income countries owned mobile phones. The pervasiveness of mobile technology can help build expansive government networks. Mobile Government (mGov) could provide citizens and businesses with extended benefits and increase overall economic growth:
Increased Access to Services: mGov could make government services more accessible to citizens and businesses, especially in remote areas where access to government offices may be limited.
Better Communication: Mobile technology can be used to improve communication between citizens, businesses, and government officials.
Cost Savings: mGov could help reduce government costs by streamlining administrative processes and reducing the need for physical infrastructure. And so on.
When in many countries people were standing with the test results printed on paper during Covid times, Ukraine developed its certificate in a smartphone. This is all because Ukraine was one of the first to think this story over. So what is digitocracy, and where does it lead to?
The Root of the Digitization
Mobile Government (m-Government) uses mobile technologies within the government administration to deliver public services to citizens and firms. These include: mobile applications, SMS and MMS services, mobile websites, mobile payments, mobile surveys.
It is quickly emerging as the new frontier of service delivery and transforming government by making public services more accessible to citizens. Governments in developing countries are increasingly making efforts to provide more access to information and assistance for citizens, businesses, and civil servants through wireless devices. However, providing strategically high-impact m-services is beset with numerous challenges – the complexity of different mobile technologies, creating secured networks to deliver reliable service, and identifying the types of services that can be easily provided on mobile devices. Therefore, the scope of this article is to identify and discuss some of the challenges and opportunities for improving government performance.
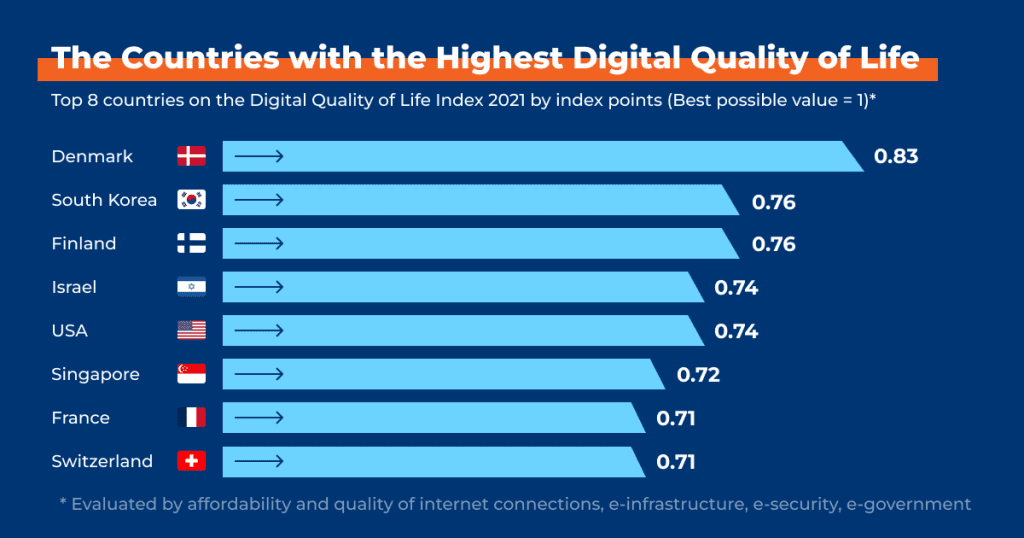 [2]
[2]The Ukrainian Сourse in Digitocracy
The Ukrainian government has been implementing various initiatives to modernize its public services and make them more accessible to citizens through mobile government (mGovernment).
One such initiative is the development of a single portal for government services and information called “Diia” (meaning “action” and “Government and Me” in Ukrainian), which can be accessed through a website or mobile application. The Diia platform allows citizens to access a wide range of government services, such as applying for passports, registering businesses, paying taxes, and more, all from a single platform. The platform also includes a digital ID system (it is called “Diia.Sign”), which enables citizens to authenticate their identity and access secure government services online.
Another important initiative is developing a mobile application called “Kyiv Smart City,” designed to improve the quality of life for citizens in the capital city of Kyiv. The application provides citizens with information about public transportation schedules, parking availability, waste collection schedules, and more, allowing citizens to report problems or issues directly to the city government.
The Ukrainian government has also been working to improve the accessibility and usability of its government services through mobile devices by conducting regular mobile device testing to ensure that its applications and websites function correctly across different devices and platforms.
The country’s administration has been making significant progress in developing and implementing mobile government services. By providing citizens with convenient and accessible state services through mobile devices, the Ukrainian government is helping to create a more efficient, transparent, and citizen-centric public administration system.
Ukraine’s Experience in Digitalization is Being Adopted all Over the World.
Already today, some European countries are adopting the experience of Ukraine in creating a digital state. Estonia, for example, is already preparing to create its own application[3] based on the Ukrainian “Diia.” By the end of the year, Estonians are planning the first release of their own application based on Diia. The Ukranian Ministry of Digitization team will share the ‘Diia’ code and approaches to UX/UI design with colleagues within the framework of cooperation.
And in Poland, the Stereo application, a new Internet bank developed on the basis of the Ukrainian Monobank, will be launched.
The Importance of Mobile Device Testing in Digitocracy
The digitalization of the state leads to one crucial point – our data requires maximum protection. And for this, proper testing of all mobile applications related to the storage of personal user data is significant.
Here is a more detailed overview of reasons why thorough testing is vital for mGov apps:
- Compatibility: Mobile testing helps to ensure that government services and information are accessible to all citizens, regardless of the type of mobile device they are using. Testing across different devices and platforms helps identify compatibility issues that may prevent some citizens from accessing government services.
- User Experience: Mobile testing helps to identify usability issues that may negatively impact the user experience of government applications. A positive UX is critical in a digitocracy where citizens rely heavily on mobile devices to access information and services.
- Reliability: Mobile testing helps ensure government applications’ reliability, ensuring they are available and functioning correctly when citizens need them.
- Trust: Mobile testing helps to build trust between citizens and government agencies. By ensuring that government applications are accessible, user-friendly, secure, and reliable, citizens are more likely to trust the government and rely on these applications.
- Loading testing: Loading testing is a crucial step in ensuring that a server can handle the expected number of users and traffic. By accomplishing load testing, performance issues can be identified and fixed before they affect real users. This ensures that the server is ready to handle expected traffic and provides a positive user experience.
- Automated testing: Automated testing can help ensure the quality and reliability of mobile government (mGov) apps by executing tests quickly and repeatedly with a high degree of accuracy. Automating testing for mGov apps can be a powerful way to ensure that your app functions as intended, improving the user experience and increasing user trust.
 [4]
[4]Conclusion
In a digitocracy, citizens can vote on policies, laws, and regulations using their smartphones. All government services would be provided through digital platforms. This would include things like healthcare, education, and social services.
However, a purely digitocratic government would likely face significant challenges and limitations. Not all citizens have access to smartphones or reliable internet, and there are concerns about digital security, privacy, and the potential for hacking.
Mobile testing is critical in a digitocracy where citizens rely heavily on mobile devices to access government services and information. By ensuring accessibility, user experience, security, reliability, and trust, mobile device testing helps to build a stronger and more effective relationship between citizens and government agencies.
As an independent testing provider, QATestLab[5] conducts comprehensive mobile application testing to find security vulnerabilities and ensure the correct operation of the application.
Thanks to an extensive pool of mobile devices, such testing allows you to ensure maximum relevance of mobile apps for any device. Here’s how you can ensure the application is secure and not worry about protecting user data.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- access to mobile phones: https://blogs.worldbank.org/governance/how-can-mobile-government-mgov-work-developing-countries
- [Image]: https://www.statista.com/chart/27883/digital-quality-of-life-index/
- own application: https://sundries.com.ua/en/estonia-will-have-its-own-diia-the-ministry-of-digital-of-ukraine-will-help-with-the-development-of-the-application/
- [Image]: https://qatestlab.com/solutions/by-focus-area/mobile-applications/?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=article&utm_campaign=Digitocracy-22022023
- QATestLab: https://qatestlab.com/solutions/by-focus-area/mobile-applications/?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=article&utm_campaign=Digitocracy-22022023
- Automation Testing for Mobile Apps: Why It’s Essential and Our Key Services: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2025/05/13/automation-testing-for-mobile-apps-why-its-essential-and-our-key-services/
- Android VS iOS: Key Differences for Mobile App Testing: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2025/02/13/android-vs-ios-key-differences-for-mobile-app-testing/
- Beyond Hours: Why Forward-Thinking Companies Choose Outcome-Based QA : https://blog.qatestlab.com/2025/08/21/beyond-hours-why-forward-thinking-companies-choose-outcome-based-qa/
Source URL: https://blog.qatestlab.com/2023/02/22/the-state-in-a-smartphone/

