- QATestLab Blog >
- QA Basics >
- Types of Software Testing >
- What is Fuzz Testing?
Note: the article was updated in June 2018.
First of all, fuzz is a random input of valid and invalid data generated for software testing. Fuzz testing or simply fuzzing is a method of testing a system by randomly altering or corrupting input data. Barton Miller, a professor at the University of Wisconsin, introduced the “fuzz” notion in 1988.
Although the technique has been around for 20 years, it has become more prevalent during the past decade due to an increased emphasis on security testing and the proliferation of tools explicitly designed for fuzzing.
Software can be fuzzed manually or automatically, but the technique is more effective when accompanied by automation and logging. Fuzzer is a program that automatically generates random data. Fuzzing is performed applying black box testing technique. It is a type of random testing.
Steps of fuzz testing
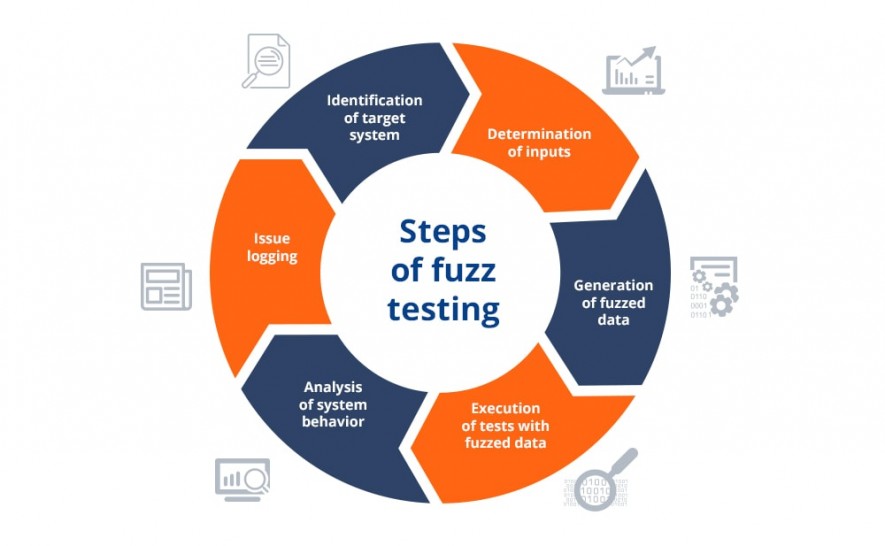
Fuzzing technique helps to detect such software bugs as memory leaks, database corruptions, security loopholes, poor search results, coding errors, system crashes, DoS (Denial of Service), XSS (Cross-site Scripting), and others.
Why Fuzzing?
- Fuzzing detects security loopholes and system vulnerabilities.
- Hackers use fuzzing technique.
- It is a cost-effective method to discover serious software bugs.
- Fuzzing is similar to automated negative testing.
But fuzz testing alone cannot detect all the security issues, and it may require too much time to provide a wide test coverage.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- No Related Posts






No Comments Yet!
You can be the one to start a conversation.