- QATestLab Blog >
- QA Basics >
- Types of Software Testing >
- Functional Testing >
- The Journey of Agricultural Software Development: How QA Fits In
The Journey of Agricultural Software Development: How QA Fits In

Modern agricultural business is characterized by innovation and technological advancement. The use of technology has significantly simplified the farming process, which was once a tedious task and required extensive manual labor. With the automation of agricultural activities, farmers can now effectively manage large areas and achieve increased efficiency.
Farming apps have been developed to aid farmers in managing their crops, predicting environmental impact, and monitoring other aspects of their farming business, such as livestock.
In this article, we will explore the critical stages of agricultural software development and the role of quality assurance (QA) in this process.
The Rise of Smart Agriculture
Before we jump into the software development stages of the agricultural application, it is crucial to recognize the possible benefits of adopting a technology-centered approach to agriculture.
Smart agriculture is an emerging field that leverages cutting-edge technologies to revolutionize traditional farming practices. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and other advanced technologies, farmers can now optimize their crop yields, conserve resources, and improve profitability.
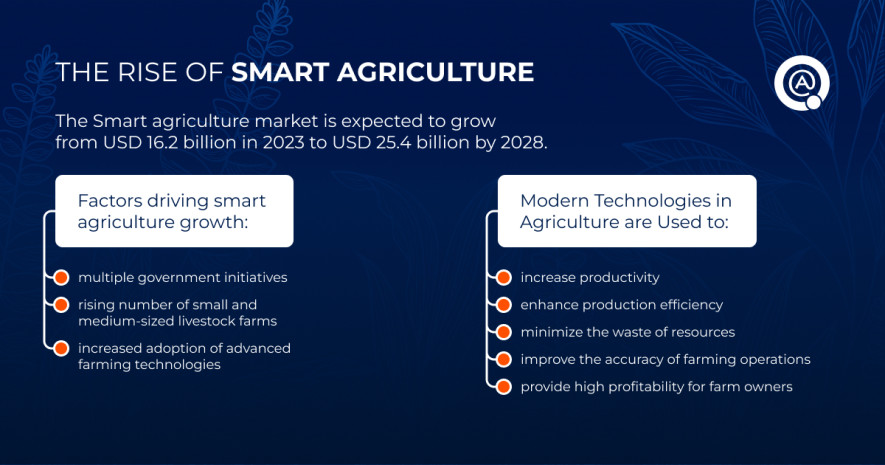
According to the Smart Farming report by Markets and Markets, increased adoption of advanced farming technologies is one of the key reasons for driving the Smart Agriculture rise.
The market is expected to grow from USD 16.2 billion in 2023 to USD 25.4 billion by 2028. The growth of the agricultural industry can be linked to two factors: the rising global population, which is exerting pressure on food supply systems, and the increasing adoption of modern farming technologies.
Modern technologies in agriculture help level up productivity, enhance production efficiency, minimize the waste of resources, and improve the accuracy and repeatability of farming operations. In addition, they provide higher profitability for farm owners.
For software developers, the smart agriculture sector presents a wealth of opportunities. The development of smart agriculture solutions requires specialized knowledge and expertise in areas such as IoT, AI, and data analytics. By keeping an eye on this sector, software developers can stay ahead of the curve and develop solutions that meet the unique needs of farmers.
Now, let’s explore the most popular features of an agriculture app.
According to research conducted by the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, the technologies most widely adopted by farmers for use in precision farming are soil sampling, GPS guidance systems, yield maps, and computers with access to high-speed internet.
Other crucial features of agricultural software include:
- Weather forecasting: Agriculture apps can provide real-time weather information to help farmers plan and make informed decisions about their farming operations.
- Irrigation management: This feature helps farmers optimize water usage by providing information on soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and other factors that affect irrigation needs.
- Crop management: This feature helps farmers manage their crops, including tracking planting and harvesting schedules, monitoring growth and development, and predicting yield.
- Pest and disease management: An agriculture app can help farmers identify and manage pests and diseases that affect their crops, by providing early detection and treatment options.
- Livestock management: This feature allows farmers to manage their livestock, including tracking animal health, breeding, and production data.
- Market prices and trading: An agriculture app can provide real-time market prices and trading information, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about selling their crops.
- Record-keeping and analytics: Agriculture apps can help farmers maintain accurate records of their farming operations, including input usage, crop yields, and financial data. The app can also generate analytics and reports to help farmers track performance and make informed decisions.
- Farm equipment management: An agriculture app can help farmers manage their equipment, including tracking maintenance schedules, fuel usage, and equipment performance.
- Labor management: This feature allows farmers to manage their workforce efficiently by tracking employee schedules, work hours, and tasks assigned. The app can also provide tools for communication between workers and supervisors and for tracking employee performance and productivity.
- Education and training: Some agriculture apps offer educational resources and training modules to help farmers learn new skills and stay up-to-date on industry trends and best practices.

Agricultural Software Development Stages
Following our discussion of the market need and specific characteristics of agricultural software, we will now discuss the stages of developing an agricultural app.
Stage 1: Planning and Requirements Gathering
This stage involves identifying the needs and conditions of the end users, understanding the business goals, and defining the scope of the project. The main objective of this stage is to create a clear and concise plan for the development process.
This stage sets the foundation for the rest of the development process. It ensures that the solution meets the needs of the end users and aligns with the business goals.
Stage 2: Design and Architecture
The second stage of software development is design and architecture. This stage involves creating a blueprint for the solution, defining the app’s architecture, and designing the user interface. The main objective of this stage is to create a clear and concise design that caters to the needs of the end users and meets business targets.
This stage lays the foundation for the agricultural solution. It ensures the product is designed to be efficient, scalable, and easy to use.
Stage 3: Development and Implementation
This phase considers coding the solution, testing the code, and integrating it with other systems. The main objective of this stage is to develop a working interface that meets the requirements of the target audience and aligns with the business goals.
It is where the product is developed and brought to life. It ensures that the software is developed according to the design specifications.

Stage 4: Testing and Quality Assurance
The fourth stage of software development is testing and quality assurance. During this phase, the app is tested for defects, bugs, and errors and ensured that it meets quality standards. The main objective of this stage is to identify and fix any issues before it is released to the end users.
Without proper testing and quality assurance, the solution can be riddled with defects and bugs, leading to costly errors and user frustration. The risks of not testing agricultural software can be significant. Without proper testing, the software may not meet the requirements of the customers, resulting in user frustration and dissatisfaction. It can also lead to costly errors, such as incorrect data analysis, resulting in crop failure and financial losses.
Step 5: Deployment and post-production
This is when the world finally sees your app. Once your developers make sure the app meets all app store requirements, you’re ready to deploy it and start getting statistics.
Your user acquisition strategy will depend on your target market. The best solution is to market your application directly to farmers with the help of traditional marketing and highly targeted digital marketing.
Agricultural app development doesn’t end with deployment. No application can survive without constant maintenance. As new technologies and frameworks emerge and the world shifts to new operating systems, your app has to go with the times.
During the maintenance phase, you can also improve your features and develop new ones — or make slight changes to your project. This will ensure your app stays relevant and brings maximum value to your users.

So, what is the role of QA during agricultural software development?
In the modern world, technology has become an integral part of the agricultural industry. Agricultural software has revolutionized the way farmers manage their crops, track their resources, and analyze their data. From precision agriculture to crop management, there are numerous software solutions available in the market that help farmers make informed decisions, save time, and increase their yields.
Without proper testing, the risks of software defects and errors can be significant, leading to costly errors and crop failure. Therefore, it is crucial to invest in proper testing and quality assurance in agricultural software development.
If you are creating or maintaining agricultural software – contact us for a customized QA solution to suit your specific needs. We will check your product for any bugs and vulnerabilities, ensuring it is ready to be used by farmers.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- When Bugs Tank Your Rankings: How QA Testing Drives SEO Performance
- ICE Barcelona 2026: Between Poker Wins and Talks on QA in iGaming
- The 2025 Cloudflare Outage: A Stress Test for SaaS Resilience
About Article Author
view more articles






No Comments Yet!
You can be the one to start a conversation.