- QATestLab Blog >
- QA Basics >
- How to Balance Nonfunctional App Aspects?
How to Balance Nonfunctional App Aspects?
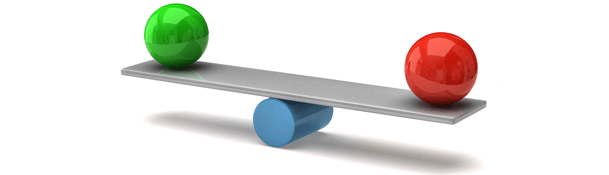
A software testing company claims that in software construction both functional and nonfunctional issues are essential. Disregarding any of them leads to software product failure in production.
So, nonfunctional issues must be paid enough attention. But it is important also not to overdo caring about them. Concerning too much about one nonfunctional aspect will lead to problems with some others.
For instance, one may want to assure top level security for a project. Implementation of it frequently leads to poor performance of an application and inconvenient user interface.
Certain companies focus on high performance of a system, but doing this they get too complex and tricky code that lacks flexibility and is hard to maintain.
If developers concentrate on creation of very easy and handy interface, security issues may be underestimated. It means that nonfunctional issues always assume tradeoffs. To avoid problems with these matters a development team must consider in the plan all the details of the development process and set criteria for an application functional and nonfunctional characteristics.
However defects of this kind can be discovered during web site testing, desktop testing or mobile application testing.
To Implement Appropriate Functional and Nonfunctional Software Aspects One Should:
- consult with the customer about what functions the constructed software must perform and what feature it must possess;
- elaborate detailed and univocal requirements both for functional and nonfunctional software aspects;
- perform functional testing along with load, usability, compatibility and security testing as early as possible in the development life cycle.
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- Why Check Nonfunctional Issues During Testing?
- Non-Functional Testing: Load and Stress
- Going Deep into Mobile Testing: Non-Functional Aspects





No Comments Yet!
You can be the one to start a conversation.