- QATestLab Blog >
- QA Basics >
- Types of Software Testing >
- Web and Desktop Testing: Key Differences Between Them
Web and Desktop Testing: Key Differences Between Them

Software applications come in various forms, each with its unique set of testing requirements. Two common categories are web and desktop testing for applications, each serving different purposes and having distinct testing challenges.
Understanding the differences between web and desktop testing is essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of your software. In this article, we’ll explore these differences and shed light on the best practices for testing in both domains.
Web Testing: The Essentials
Web applications, also known as web apps or online software, are accessed through web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari. Some popular web apps are Gmail,
Facebook, Google Docs, Trello, and Netflix
They are designed to run on various platforms and devices with an internet connection, making them highly accessible.
When it comes to testing web applications, there are several must-test areas our QA experts identify:
Cross-browser compatibility testing is done to ensure that the web application functions correctly across different browsers and versions. Each browser interprets web pages differently, which can lead to compatibility issues.
Responsive design testing involves evaluating how the application behaves on various screen sizes and resolutions to guarantee a seamless user experience.
Performance testing assesses how well the app performs under various load conditions, ensuring it remains responsive and stable even during peak usage.
Security checks are vital to identify vulnerabilities and protect sensitive user data.
Web apps are susceptible to a wide range of security threats, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and data breaches.
Web Application Testing Case Study
Background:
The client developed a conference application that allowed users to create conferences and various negotiation rooms. They needed to ensure that the application worked flawlessly across different browsers on PCs and mobile devices, even in conditions with unreliable internet connectivity.
Challenges:
- The application needed to be compatible with a wide range of web browsers to cater to a diverse user base.
- The client required thorough testing on various mobile devices to ensure a seamless user experience, especially in areas with poor internet connectivity.
- The client wanted to measure the Frames Per Second (FPS) on different PC configurations to ensure optimal performance.
Testing Approach
To address the client’s requirements, we adopted the following testing approach:
Our specialist conducted comprehensive testing of the application on different web browsers, including popular ones such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Safari. This ensured that the application functioned correctly and consistently across various browser environments.
Then, the tester executed tests on a wide array of mobile devices, considering both Android and iOS platforms. The testing covered different screen sizes, resolutions, and operating system versions. Special emphasis was placed on testing in areas with limited network connectivity.
Additionally, we assessed the application’s performance by measuring FPS on various PC configurations. This involved testing on both high-end and low-end hardware to guarantee smooth operation for all users.
Results
During the testing phase, the test engineer identified several issues and provided the following results to the client:
- We discovered graphical defects within the application, such as misaligned elements, image rendering issues, and inconsistent design elements. These were reported with detailed descriptions for the development team to address.
- Functional issues were identified, including errors in conference creation, room management, and real-time communication features. The tester reported these bugs with clear steps to reproduce them.
- The usability testing revealed user interface problems and inconsistencies, making it difficult for users to navigate and utilize the application efficiently. Detailed usability reports were provided to guide the client’s design improvements.
- We also conducted FPS measurements on different PC configurations and provided the client with a performance benchmark report. This allowed the client to optimize the application for smooth performance across a wide range of devices.
By collaborating with QATestLab, the company not only fixed existing problems but also gained valuable insights into their application’s performance and usability on diverse devices and browsers, thus ensuring a successful and reliable product launch.
Desktop Testing: A Different Realm
Desktop applications, on the other hand, are software programs installed and run locally on a user’s computer. Unlike web apps, desktop applications don’t rely on browsers for operation. A few examples of desktop applications are Microsoft Word, Adobe Photoshop, Mozilla Firefox, and Spotify.
Our QA specialists identify these crucial aspects of desktop testing:
Operating system compatibility testing ensures the application runs smoothly on different OS versions and configurations. Desktop applications must be compatible with specific operating systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux).
Installation and update testing includes verifying the installation process, update mechanisms, and backward compatibility. Unlike web apps, desktop apps require installation and may have frequent updates.
User interface (UI) consistency checks are done to ensure that the interface elements, such as buttons and menus, function as expected.
Performance and resource usage testing involves monitoring CPU and memory usage to ensure the app doesn’t slow down or crash other processes. Desktop applications can consume significant system resources.
Desktop Application Testing Case Study
Background
The importance of accurate and comprehensive documentation in healthcare software cannot be overstated. The Patient Entry Desktop application was designed to streamline patient data management, but it was essential that the accompanying documentation was equally logical, consistent, and informative.
Challenges:
- Ensuring that the documentation was clear, accurate, and free of errors was paramount. Documentation quality directly influences user understanding and the application’s overall reliability.
- Given the diverse nature of the documentation, testing had to encompass multiple levels of complexity, from grammar and spelling checks to assessing logical consistency and eliminating ambiguities.
- High-quality documentation was expected to correlate with stable system operation and an overall superior application experience for users.
Testing Approach
To meet the client’s objectives, QA specialists from QATestLab performed the following testing activities:
- Spelling and Grammar Checks
Automated spelling and grammar checks were performed on all documentation materials, including user manuals, help guides, and instructional documents. This ensured that basic language errors were identified and rectified.
- Manual Inspection
Expert testers manually inspected the documentation for logical consistency, clarity, and informativeness. Ambiguous expressions, inconsistencies, and incompatibilities were identified and addressed.
- Usability Testing
Usability testing of the documentation was conducted to assess its effectiveness in helping users understand and navigate the application. Feedback from usability tests was used to refine the documentation further.
Results
Through rigorous testing, the following deliverables were provided to the client:
- The documentation was transformed into a logically structured, consistent, and highly informative resource. Users could rely on it to understand and utilize the ” application effectively.
- As the quality of documentation improved, users gained a clearer understanding of the application’s features and functionalities. This resulted in more efficient usage, reducing the likelihood of errors and contributing to the system’s overall stability.
- The application’s reputation for quality and reliability was reinforced, ultimately contributing to higher user satisfaction and trust.
The collaboration between testing experts and app developers ensured that users had access to clear, logical, and consistent documentation, which, in turn, translated into a more efficient and reliable healthcare administration tool.
Web and Desktop Testing: Let’s Compare
Now that we’ve grasped the concepts of desktop and web application testing, let’s explore their distinctions. We’ll examine the following criteria to shed light on the key differences:
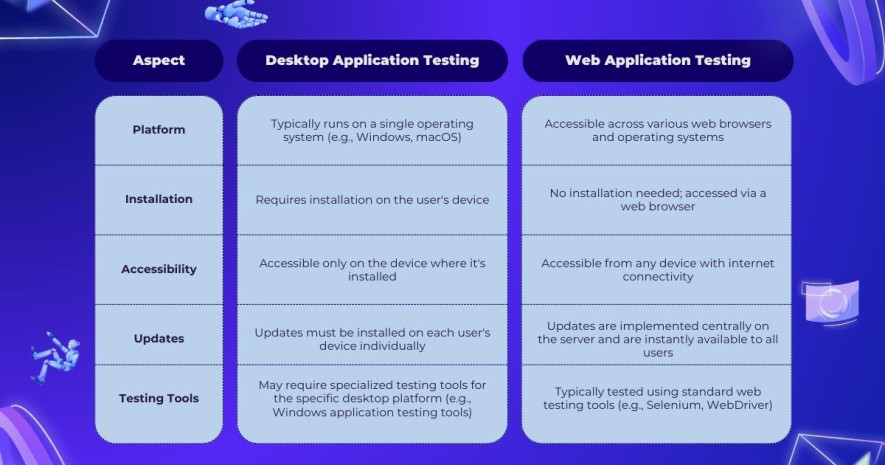
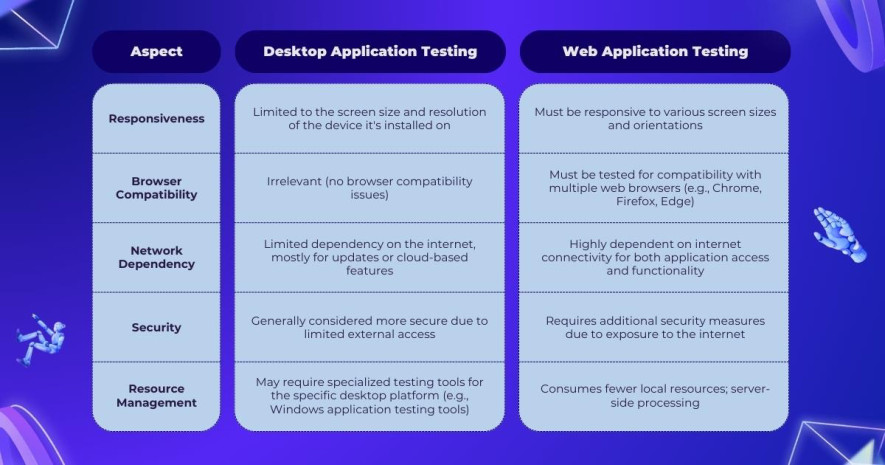
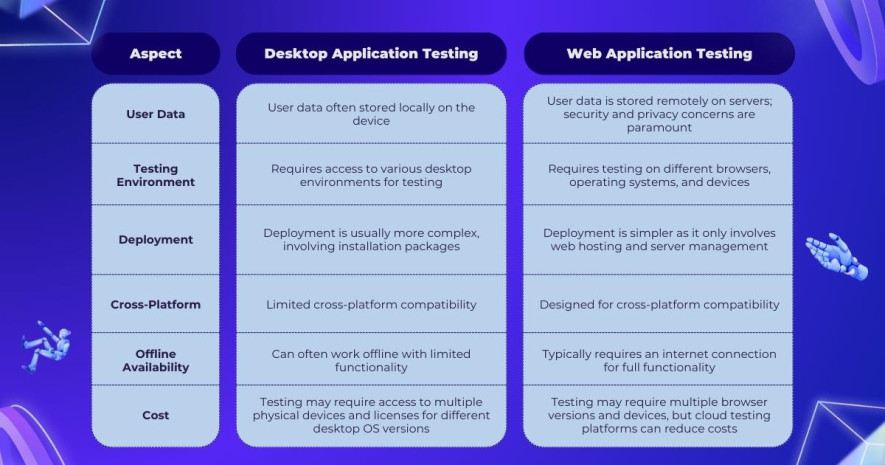
Understanding the differences between web and desktop testing is crucial for delivering a seamless user experience.
Web testing emphasizes cross-browser compatibility, responsive design, and security, while desktop testing focuses on operating system compatibility, installation procedures, and resource management.
By recognizing these distinctions, businesses can tailor their strategies to ensure the optimal functionality and reliability of both web and desktop applications, ultimately enhancing user satisfaction.
Conclusion
The world of desktop and web app testing is wide and constantly evolving. New cross-platform capabilities, such as deep linking web links to open mobile apps or optimizing battery usage of mobile apps, are constantly being developed to enhance business value for end-users.

To ensure high-quality testing of applications across platforms, it is important to understand how users will be using the app on each platform, what would be the most likely scenarios they would encounter, and then build these test points into the test cases from the beginning.
At QATestLab, we provide end-to-end testing for all applications built on various frameworks.
Learn more about our testing capabilities and how they can help your company. Just contact us today!
Learn more from QATestLab
Related Posts:
- When Bugs Tank Your Rankings: How QA Testing Drives SEO Performance
- ICE Barcelona 2026: Between Poker Wins and Talks on QA in iGaming
- The 2025 Cloudflare Outage: A Stress Test for SaaS Resilience
About Article Author
view more articles